Why go tobacco-free?
Many people are unknowingly contributing to the global tobacco epidemic.
Sign The Pledge
See The Business Case
Hear From Leaders in Finance
There are many controversial companies and challenging sectors that need to be considered when building a sustainable finance framework. Among them, tobacco stands out as an exception that demands the strongest possible response from the finance sector – exclusion from financing and investment.
These three key facts articulate why:
No safe use
There is no safe level of tobacco consumption. When used as intended, tobacco will have contributed to the early death of two out of three smokers. (Source)
UN Tobacco Control Treaty
Due to the profound scale of the negative impact of tobacco – an estimated eight million deaths per year (Source) – tobacco is the focus of the world’s only global health treaty – the United Nations’ Tobacco Control Treaty – which has been ratified by 183 Member States covering almost 90% of the world’s population.
Engagement is futile
The World Health Organization has declared, “The tobacco industry is not and cannot be a partner in effective tobacco control” (Source) and “Engagement with the tobacco industry is contrary to the United Nations’ systems, objectives, fundamental principles and values.” (Source) Positive influence of the industry through professional engagement is futile, as the only acceptable outcome would be for tobacco companies to cease their primary business.
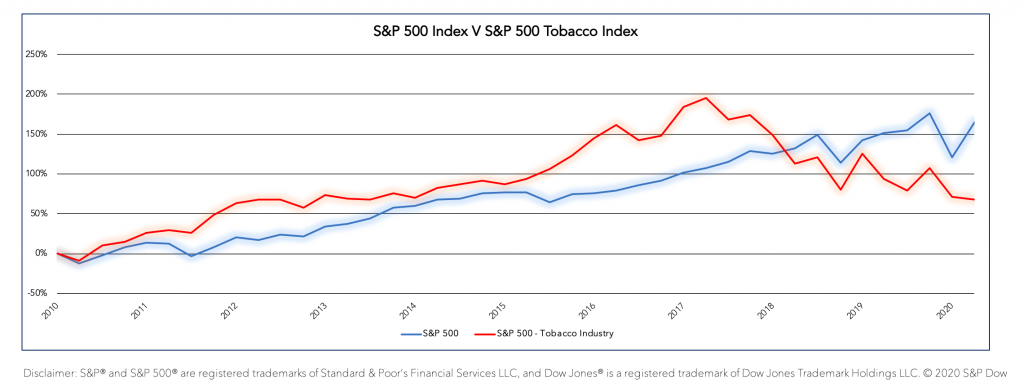
A combination of financial risks has seen share prices drop since 2017
1. Regulatory Risk
In 2004 the World Health Organization established the Framework Convention on Tobacco Control – otherwise known as the United Nations’ Tobacco Control Treaty – the world’s only global health treaty. 183 Member States (Governments) have signed and ratified the treaty which compels them to implement a comprehensive suite of evidence-backed policies that reduce tobacco consumption.
2. Litigation Risk
Major class actions against tobacco companies pose considerable financial risk.
3. Supply chain risk
Almost no cigarette can be guaranteed to be free from child labour. (Source) This issue will receive increasing attention as scrutiny on global supply chains intensifies.
4. Environmental risk
Tobacco causes environmental destruction spanning land clearing, deforestation, pesticide use and water contamination, however, the issue receiving most attention at present is that cigarette filters are the number one ocean plastic. (Source)
5. Reputational risk
Investment in tobacco companies implies endorsement of the product itself and of the industry as a whole. Individuals and organisations are increasingly evaluating and reflecting on the alignment between their own values and those of the companies with whom they do business.